Fish Farm design: Fish farming is a rapidly growing industry that provides a healthy and sustainable source of protein for millions of people around the world. If you’re interested in starting your own fish farm, there are a few key things to consider when it comes to design, construction, and management.
Design, Location of Fish Farm
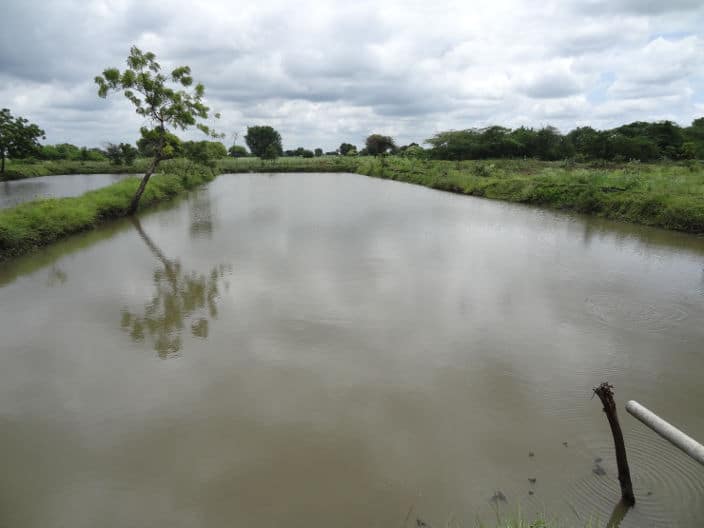
A fish farmer needs several kinds of ponds for rearing fish, as well as a farm layout. The quantity and size of the ponds needed depend on the species of fish that will be raised. When building a fish farm, the location must be chosen with care for drainage, water availability, and soil quality. Fish farm location Choosing a proper location for the farm is crucial for both fish farming success and construction economy. These are
Topography
It refers to the area’s surface features, which are significant for both development and ongoing upkeep. A broad valley with gentle slopes or a bowl-shaped location with highlands on three sides and a limited exit on the fourth is the best topography for a fish farm. Given the availability of an appropriate water supply and the desired type of soil, such a location could be chosen for the construction of the farm. These kinds of places are easily transformed into sizable ponds by building an embankment that blocks the discharge. It could be required to seal the bottom to stop leaks and dress it up to get it to a uniform depth.Construction plan should include provision for handling normal flow of water and also for complete drainage.
Soil type
To prevent seepage, the soil needs to be impermeable. Areas with rocky, sandy soil and limestone should be avoided. Generally speaking, silty and heavy clays work well, and fish ponds built in these types of soils hold water for extended periods of time because the only way water is lost is by evaporation. Although stocking ponds should not be built in porous soil, nursery and rearing ponds can be built because they only need to hold water temporarily. If the soil is porous, it can also be addressed by applying many layers of soil sealant or clay to the bottom. A pond with healthy soil would be fertile. Soil analysis is the process by which soil is correctly identified.
Water supply
The availability of adequate supply of water is an important requisite for site selection. The dependable sources of water supply are-a. lake and reservoirs (b) springs (c) river (d) streams (e) canals (f) surface runoff water and (g) canals.
Big tanks, reservoirs and lakes are perhaps the best source of dams provides the cheapest water for the farm. Good springs do not dry up in summer and form a dependable source of water. Stream, rivulets and canals are also a satisfactory source of water, provided the flow is enough to fill the ponds a constant water level is maintain and only a little silt is carries so that clear water is available even during the rainy season. Small streams that are likely to b over flooded during rain are should be avoided because the water would carry heavy silts reducing the fertility of pond. The water of rivers supplied by canals is also satisfactory and dependable source. ‘Fish Farm’
Layout of the fish farm: planning and construction of fish farm:
Before starting the construction, the layout planes have to be drawn for the location design and the number of various types of ponds. The size of the farm. Subsistence fishing, only small size farm is enough but commercial and experimental farms larger area is needed for constructing breeding, nursery, rearing, and stocking ponds. various farms buildings such as laboratory, store house, watch man huts, residential quarters etc. are also to be constructed. A fish farm consists of 4 types of ponds-
Hatching pits
Hatching pits or spawning ponds are small tanks usually 8’x4’x2’ are used for hatching fertilized eggs. A continuous but slow flowing water is desi able for aerating the eggs. A smaller cloth tanks called HAPA of fine net cloth is fixed up.
Nursery ponds
Nursery ponds are 50’x50’x4’ and mat be seasonal so that they dry up during summer season. This helps in eradication of fish enemies and in increasing productivity.
Rearing tanks
Rearing ponds may be seasonal or perineal and are used for rearing advance fry for2-3 months. These ponds are made up of long and narrow gently sloping to facilitate netting.
Stocking ponds
Stocking ponds are large perineal tanks more than 6’ deep. They are long and constructed for facilitate netting.
Besides above a few marketing ponds may also be provided in a farm for keeping fish ready for market. For pond breeding species, breeding ponds are necessary and in some cases marketing ponds maybe arranged in one or two rows and with a space between ponds. Long narrow and deeper ponds are better than smaller ones.
Embankment of Fish pond
An ideal fish pond should have an embankment that slopes 2:1. The embankment should also have an extra height to prevent the waves for overflowing. Drainage is very important for proper management of ponds. There must be inlets and outlets. The drain pipes should be large enough for quick drainage. The inlet pipes should be above the water level and provided with some kind of screen to prevent entrance of and escape of fish from the ponds. The fencing is necessary to prevent cattle. The swamp can be converted for culture of air breathing fishes. ‘Fish Farm’
Managenent of pond
The productivity of ponds depends upon its soil base and can be greatly enhanced by controlling of vegetation, cleaning of pond bottom, liming and fertilization. All undesirable plants and weeds must be removed regularly by using various methods of weed control. The pond should be emptied, dried and cleaned at suitable interval. Ponds that not dried gradually lost their productivity. Lack of proper maintenance causes siltation of the ponds. The mud accumulates raising the level of bottom of the ponds. The natural productivity of a pond can be increased by using fertilizer which provide nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
Organic and Inorganic fertilizers used for improvement of pond:
Organic Fertilizer: Organic fertilizer carries almost all nutrients required by the fish. The liquid manure from the stables is very beneficial and stimulates the growth of the zooplankton, phytoplankton as well as filamentous algae. Liquid manure is released in small quantity only in deeper parts of the pond and give high yield of fish, use of guano also increased productivity. Farm manure considering of cow dung and pig dung is used in fish culture. Sewage is also considered good fertilizer with nitrogen and phosphorous. sewage is first diluted before mixing with pond water. It enhances the production of plankton and growth rate of fish. organic fertilizer increased the fish production, but they may cause oxygen deficiency and infections. It is better to spread them in small quantities and at regular intervals. Soyabean meal, cotton seed meal, mustard oil cake etc. are also used. Mustard oil cake with cow dung is used as pond fertilizer. In Bengal green grass with dry cow dung, poultry manure and oil cake used for manuaring fish pond (compost after 3 months) a dose of 5000 kg/hac. Compost is rich in growth of plankton. ‘Fish Farm’
Inorganic fertilizers: Purpose of fertilization of the pond to increased the productivity by increasing the natural food available various inorganic fertilizer is used, such as super phosphate to increase the production of fish. Another nitrogenous inorganic fertilizer is sodium nitrate, ammonium sulphates, ammonium nitrate, ammonium carbonate, urea etc. are used to fertilized the pond. Ammonium sulphate helps in phytoplankton biomes and heavy growth of zooplankton the use of inorganic salts depends upon the soil and the water condition of the ponds. ‘Fish Farm’
Liming: The first step in fertilization of a pond is applicable of lime. Quicklime (CaO) is generally used and it increased the PH of water and act as an antiparasitic substance. It kills the bacteria and other parasites. Lime is used when PH is very low, when the soil is too muddy and organic matter is so high a dose of 100-2oo kg/hac of lime is necessary and must be used in every year regularly. It prevents the gill rot disease of fish. Heavy soil needs more lime than sandy soil. Lime is generally spread on pond bottom 10-15 days before stocking the pond with fish. It is better to leave the pond dry for at least two weeks after liming.
Artificial feeding
Fish production can be increased by artificial feeding. This should be simple and cheap. Such type of food is whole grain, floor, rice bran, oil cake and kitchen waste, fish meal, meat, and blood are also useful. The food can be kept in basket or spread in the water.
Fishing and harvesting
This is done by draining the pond or netting. By draining, harvesting is complete and predators can be eliminated. Much less labour is required and the pond can be dried cleaned, repaired and soil enrich by fertilization. But all water is loss by draining. However, if the pond is constructed in a row loss of water can be avoided and ponds are drained by turns.