Cell Organelles: Cells are the basic units of life and they are incredibly tiny. Most cells are microscopic and can only be seen with a microscope. Even though they are small, they are very complex and have many different parts, just like our bodies do. These parts are called organelles and each one has a specific job to do in order to keep the cell alive and functioning. There are many different organelles in a cell, but some of the most important ones mentioned here for the study by using charts, models, slides and electron miscrograph:
Cell Organelles
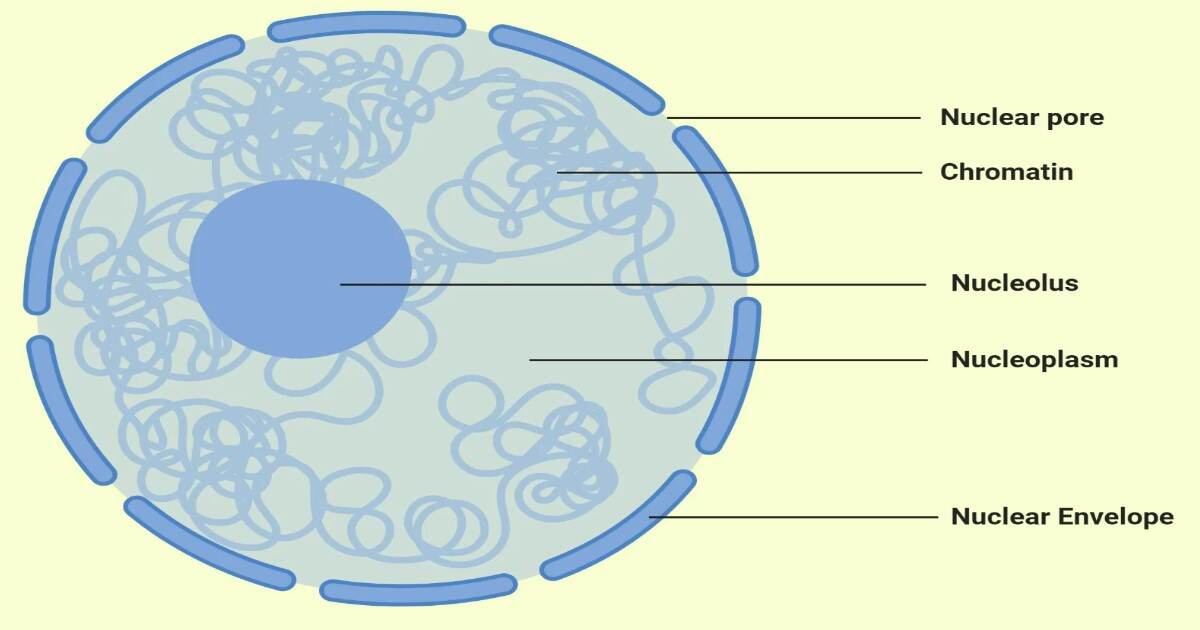
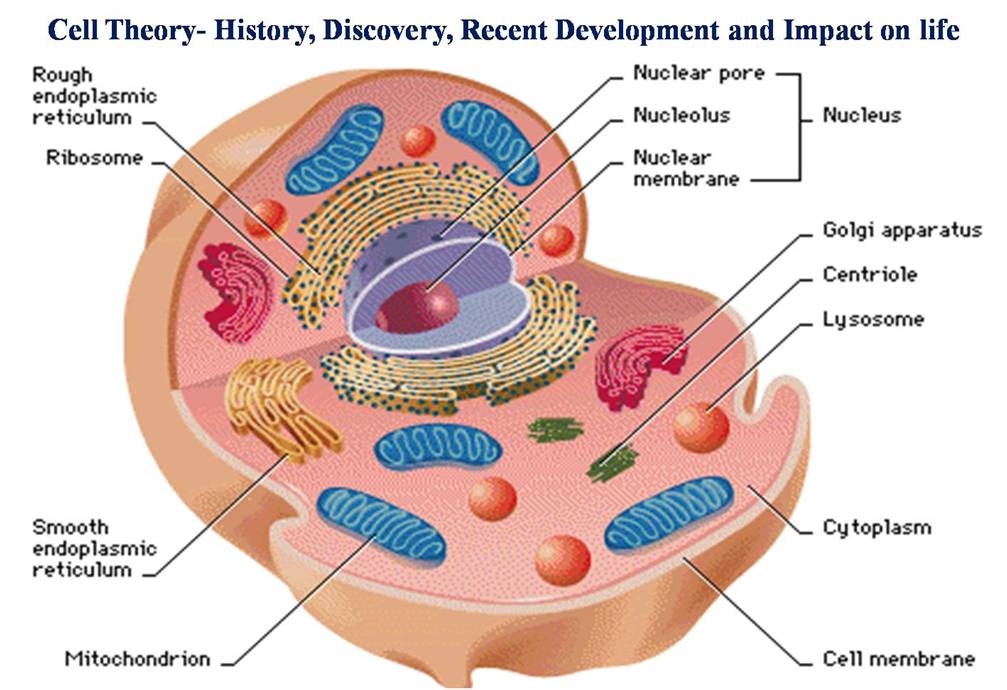
1. Nucleus
Comments
- Nucleus is covered by a double layered membrane known as nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope.
- Nuclear envelope has pores through which these nucleic acids and proteins pass in and out of the nucleus. ‘cell organelles‘
- Within the nucleus is present a dark staining nucleolus.
- Dense substance known as chromatin is present in the nucleus which during division transforms into chromosomes.
- Hereditary material or the Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are present in the nucleus.
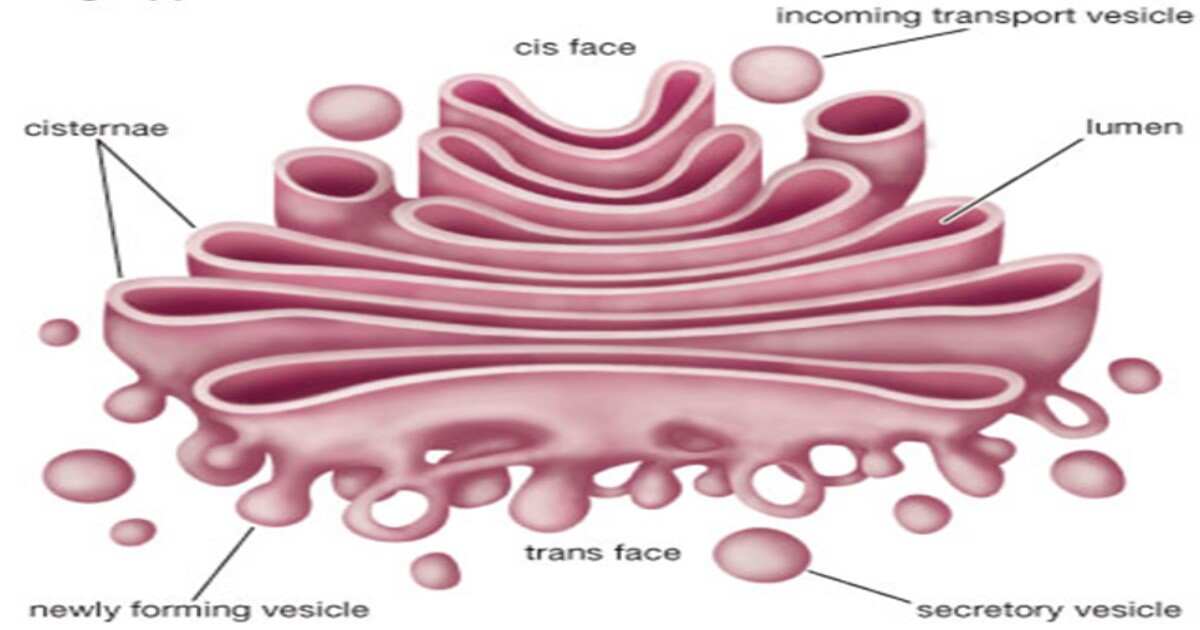
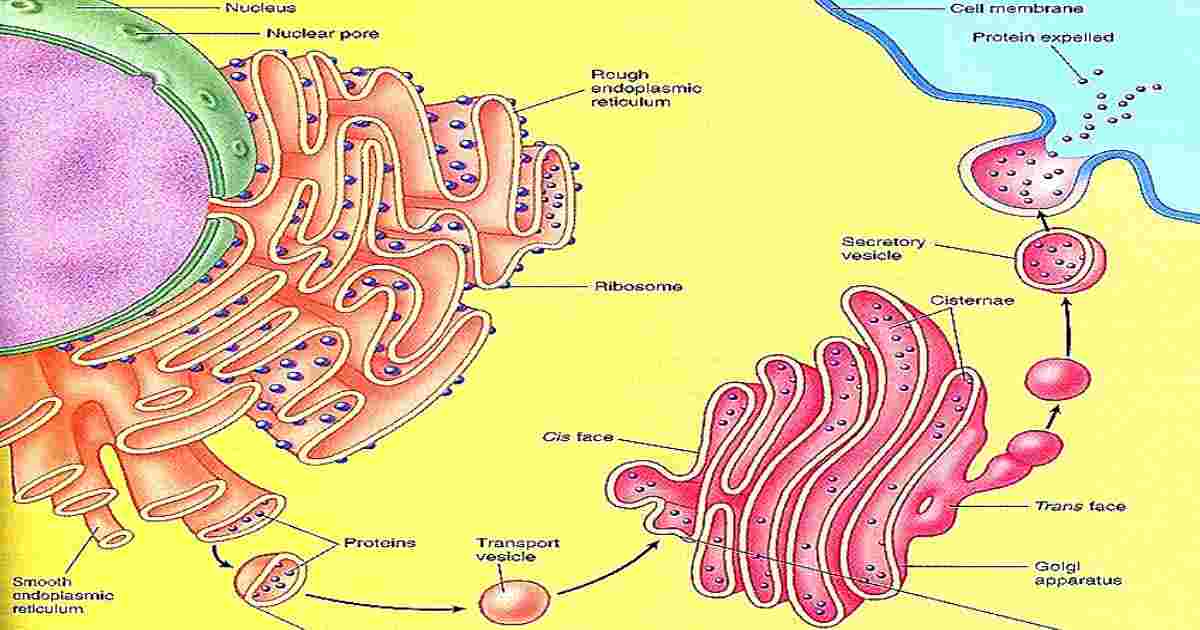
2. Golgi body
Comments
- Double membranous structure.
- The Golgi is composed of membrane-bound stacks known as cisternae.
- Between four and eight cisternae are usually present.
- The cisternae stack has five functional regions: the cis-Golgi network, cis-Golgi, medial-Golgi, trans-Golgi, and trans-Golgi network.
- The trans face of the trans-Golgi network is the face from which vesicles leave the Golgi.
- New cisternae form at the cis-Golgi network. ‘cell organelles’
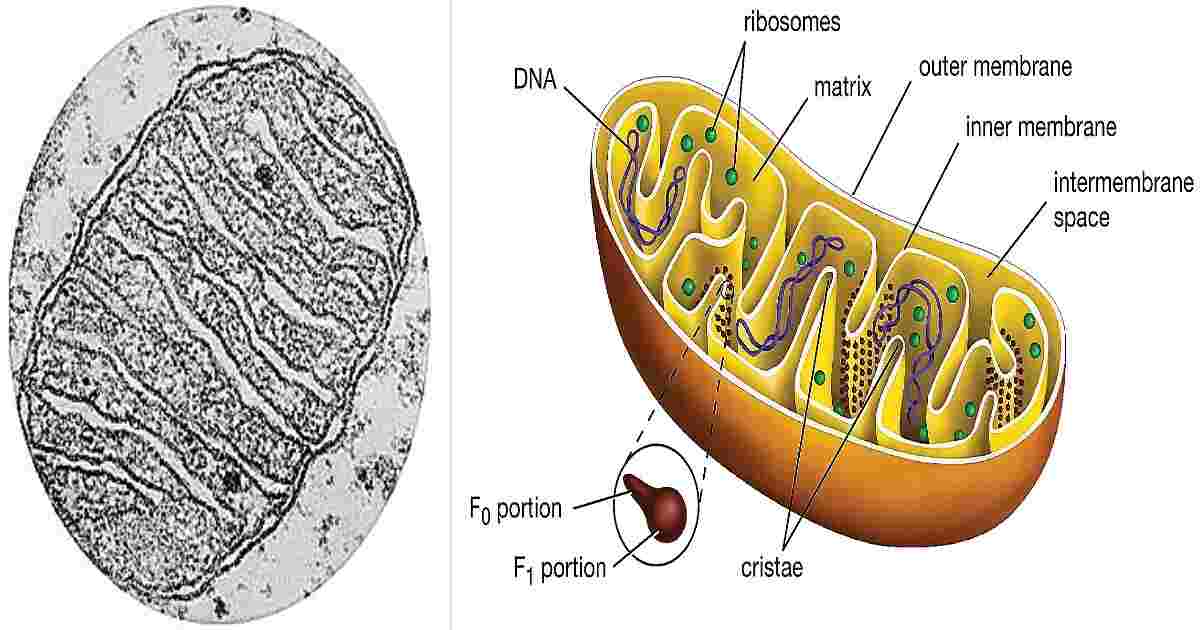
3. Mitochondrion
Comments
- A mitochondrion contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins.
- The two membranes, however, have different properties.
- These organelles range from 0.5–10 micrometers (μm) in diameter.
- They are known as the ‘Power House’ of the cell as most of the energy is supplied to the cell by mitochondrion in the form of ATP.
- Inner membrane is thrown into folds and projections called as cristae.
- Mitochondria are the sites of the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation, which result in the formation of ATP. ‘cell organelles’
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Comments
- The general structure of the endoplasmic reticulum is an extensive membrane network of cisternae (sac-like structures) held together by the cytoskeleton.
- There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum ‘Rough’ and ‘Smooth’.
- Ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum due to which it has rough appearance and hence its name.
- Smooth ER is devoid of ribosomes hence it has smooth appearance.
- The membrane of the ER is continuous with the outer layer of the nuclear envelope.
5. Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell.
- They use instructions from the cell’s DNA to make proteins, which are essential for all cell functions.
- Ribosomes are made up of RNA and protein and can be found free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
6. Lysosomes
- Lysosomes are the cell’s waste disposal units.
- They contain enzymes that break down old or damaged cell parts, food particles, and foreign invaders.
- Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs filled with enzymes.