Fasciola hepatica: Fasciola, often known as the common fluke, is a parasitic flatworm that lives in the liver and bile passages of vertebrates, including dogs, pigs, sheep, cattle, and rabbits.
Fasciola hepatica
An illness known as fascioliasis, or liver rot, is brought on by the several species of Fasciola, such as F. hepatica, the liver fluke of sheep, and F. gigantica, also known as F. indica, the liver fluke of cattle. These species seriously harm the liver tissues and bile passageways. Fascioloides magna, Opisthorchis sinensis, and Fasciololepsis buski are among the other related species. The Fasciola narrative that follows, however, is about the species hepatica.
FASCIOLA HEPATICA (SHEEP LIVER FLUKE)
Phylum …. Platyhelminthes
Class …. Trematoda
Order …. Digenia
Genus …. Fasciola
Species …. hepatica
HABIT AND HABITAT
Fasciola hepatica (L., fasciola = small bandage; Gr., hepar =liver), the sheep liver fluke, lives as an endoparasite in the bile passages of sheep. Its life cycle is digenetic, i.e., completed in two hosts (a primary vertebrate host, the sheep and a secondary or intermediate invertebrate host, the gastropod mollusc).
The adult parasite is found in the primary host, while a part of its life cycle as larval stages are found in the invertebrate host. Fasciola hepatica, in addition to sheep, also infects other vertebrates like goat, deer, horse, dog, ass, ox and occasionally man. Its secondary hosts are either Planorbis sps, Bulinus sps., or Limnaea truncatula, all being freshwater gastropod molluscs. Fasciola hepatica is worldwide in distribution, particularly sheep and cattle raising areas are the primary zones where human beings are also infected. Its other Indian species, F. gigantica (= indica) is found in the bile passages of buffaloes, cow, goats and pigs.
STRUCTURE
Shape, size and colour
The body of F. hepatica is thin, elongated, oval, leaf-shaped, and dorsoventrally flattened. Its dimensions are roughly 4 to 12 mm in width and 25 to 30 mm in length. The body tapers both anteriorly and posteriorly at this point, where the maximum width occurs. The anterior end is slightly rounded, while the posterior end is bluntly pointed. The width of F. indica is largest in the middle of the body, and the back end is rounded. It is typically pink in color, but because of the host’s bile that has been swallowed, it looks brown.
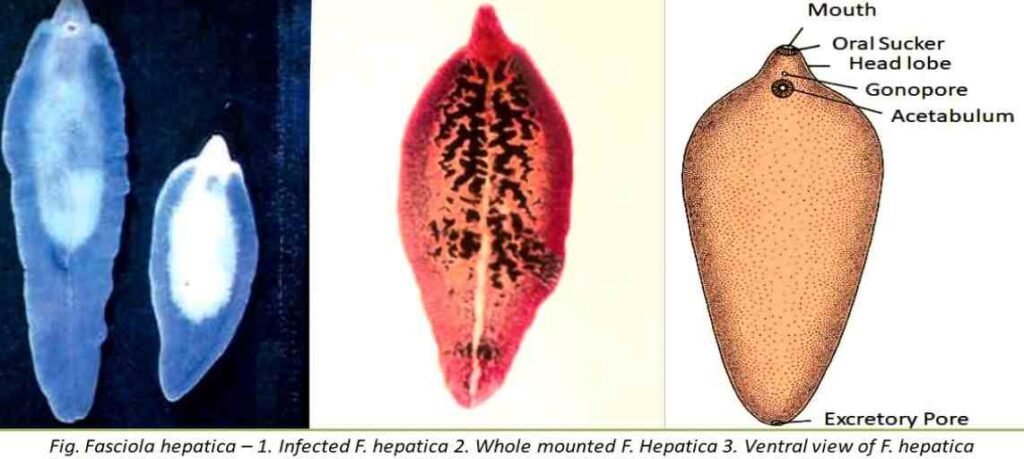
External morphology
The anterior end of the body is distinguished into a triangular oral cone or head lobe giving it a shouldered appearance. The head lobe, at its tip, bears a somewhat triangular aperture called mouth.
There are two muscular suckers : an oral sucker at the anterior end encircling the mouth, and a large ventral sucker or acetabulum situated mid-ventrally about 3 to 4 mm behind the oral sucker. The suckers are cup-like muscular organs meant for attachment to the host by vacuum.
In addition to mouth aperture, there are two permanent apertures on the body ; one situated mid-ventrally in front of the ventral sucker is the common genital aperture or gonopore, and the other is situated at the posterior end of the body called the excretory pore. In addition to these apertures, a temporary opening of Laurer’s canal appears during the breeding season on the dorsal surface just anterior to the middle of the body. Anus is wanting because alimentary canal is incomplete.