Abnormal constituents of urine: Urinalysis, a diagnostic test that aids healthcare professionals in identifying and diagnosing various medical disorders, includes the physical and chemical analysis of aberrant substances in a urine sample. Urine can contain a variety of abnormal substances, such as proteins, blood cells, crystals, glucose, and many more. The physical and chemical analysis of abnormal constituents of urine components is summarized as follows.
Physical and chemical examination of abnormal constituents of urine:
The physical and chemical abnormal constituents of urine as follows:
Physical examination
The physical examination of a urine sample can provide information about the following:
1. Color: Normal – Depending on nutrition and hydration levels, urine’s color might range from pale yellow to amber. Abnormal – Different disorders can be indicated by unusual colors. For instance, red or pink urine can be a sign of blood, while brown or black pee might be a sign of problems with the liver or kidneys.
2. Appearance (Clarity): Normal urine is clear or hardly cloudy and abnormal urine is cloudy and could indicate an infection, crystals, or other problems.
3. Odor: : The normal urine smell is somewhat akin to ammonia while urine that smells foul or sweet may be abnormal and signify a medical issue.
4. Specific gravity: The specific gravity of urine is a measure of how concentrated it is. Normal specific gravity ranges from 1.003 to 1.030. Low specific gravity can be caused by diabetes insipidus or excessive fluid intake. High specific gravity can be caused by dehydration or kidney disease. ‘Abnormal constituents of urine’
5. pH (acidity or alkalinity): The normal pH of urine can vary, but it is normally a little acidic (6.0) and abnormal change in pH levels might be a sign of kidney or metabolic problems.
Chemical examination
The chemical examination of a urine sample can be used to detect the presence of abnormal constituents of urine, such as:
1.Glucose: Glucose is not normally present in urine. The presence of glucose in urine (glycosuria) is a sign of diabetes mellitus.
2. Protein: Protein is not normally present in urine. The presence of protein in urine (proteinuria) can be a sign of kidney disease.
3. Blood: Blood is not normally present in urine. The presence of blood in urine (hematuria) can be caused by a variety of conditions, including kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and cancer.
4. Bile pigments: Bile pigments are not normally present in urine. The presence of bile pigments in urine (biliuria) can be a sign of liver disease or gallstones.
5. Ketone bodies: Ketone bodies are not normally present in urine. The presence of ketone bodies in urine (ketonuria) can be a sign of uncontrolled diabetes or starvation.
6. Urobilinogen and bilirubin: Urine typically contains trace levels of urobilinogen and bilirubin. Elevated levels are abnormal and may be a sign of liver or gallbladder issues.
7. Crystals: Normal urine often doesn’t include crystals while crystals may be an abnormal sign of metabolic problems or kidney stones. ‘Abnormal constituents of urine’
8. Nitrites and Leukocyte Esterase: Normal urine usually doesn’t contain these and abnormal urine positive readings may suggest a urinary tract infection.
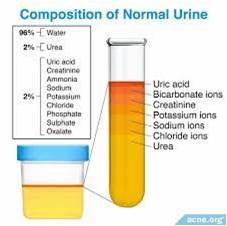
This resource explains the physical examination of urine samples including volume, specific gravity, color, appearance, odor, and pH. It also covers the chemical examination of urine samples for normal constituents such as urea, uric acid, creatinine, chloride, phosphate, bicarbonate, sulphate, ammonia, oxalates and abnormal constituents such as proteins, sugar (glucose & others), ketone bodies, bilirubin, bile salts & blood
Conclusion:
A urine sample is obtained and analyzed using a variety of techniques and tools, including dipstick testing, microscopic examination, and chemical reagents, to carry out these physical and chemical exams. The outcomes of these tests can offer useful information for diagnosing and tracking a variety of medical disorders, enabling healthcare professionals to suggest suitable treatments or additional research as necessary. An experienced healthcare expert should always interpret the results.