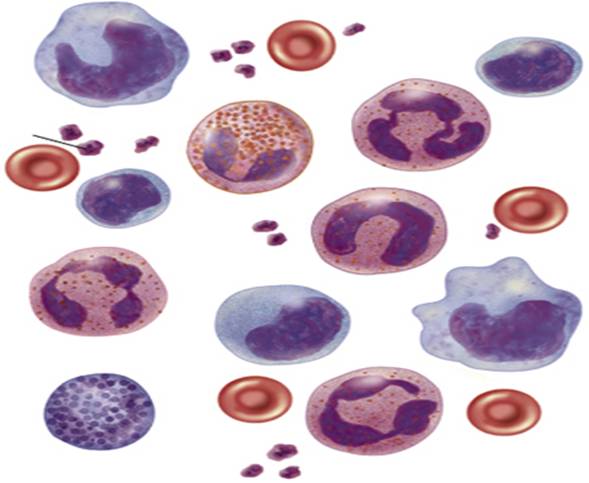
Blood smear: Studying a blood smear for a differential white blood cell (WBC) count is a crucial diagnostic procedure in the field of hematology. This technique involves preparing a thin layer of blood on a glass slide, staining it, and then observing the different types of white blood cells present under a microscope. The purpose of this analysis is to determine the relative percentages of different types of white blood cells in the sample, which can provide valuable insights into a patient’s health.
Types of white blood cells (WBCs)
The five main types of WBCs are:
- Neutrophils: These are the most common type of WBC and help fight infection.
- Lymphocytes: These cells help the body fight infection and disease.
- Monocytes: These cells engulf and destroy bacteria and other foreign invaders.
- Basophils: These cells release histamine, which helps the body respond to allergic reactions.
- Eosinophils: These cells help fight parasitic infections.
The normal range for the differential WBC count varies depending on the age and sex of the person. However, a healthy adult typically has the following percentages of each type of WBC:
- Neutrophils: 40-70%
- Lymphocytes: 20-40%
- Monocytes: 2-8%
- Basophils: 0-1%
- Eosinophils: 0-4%
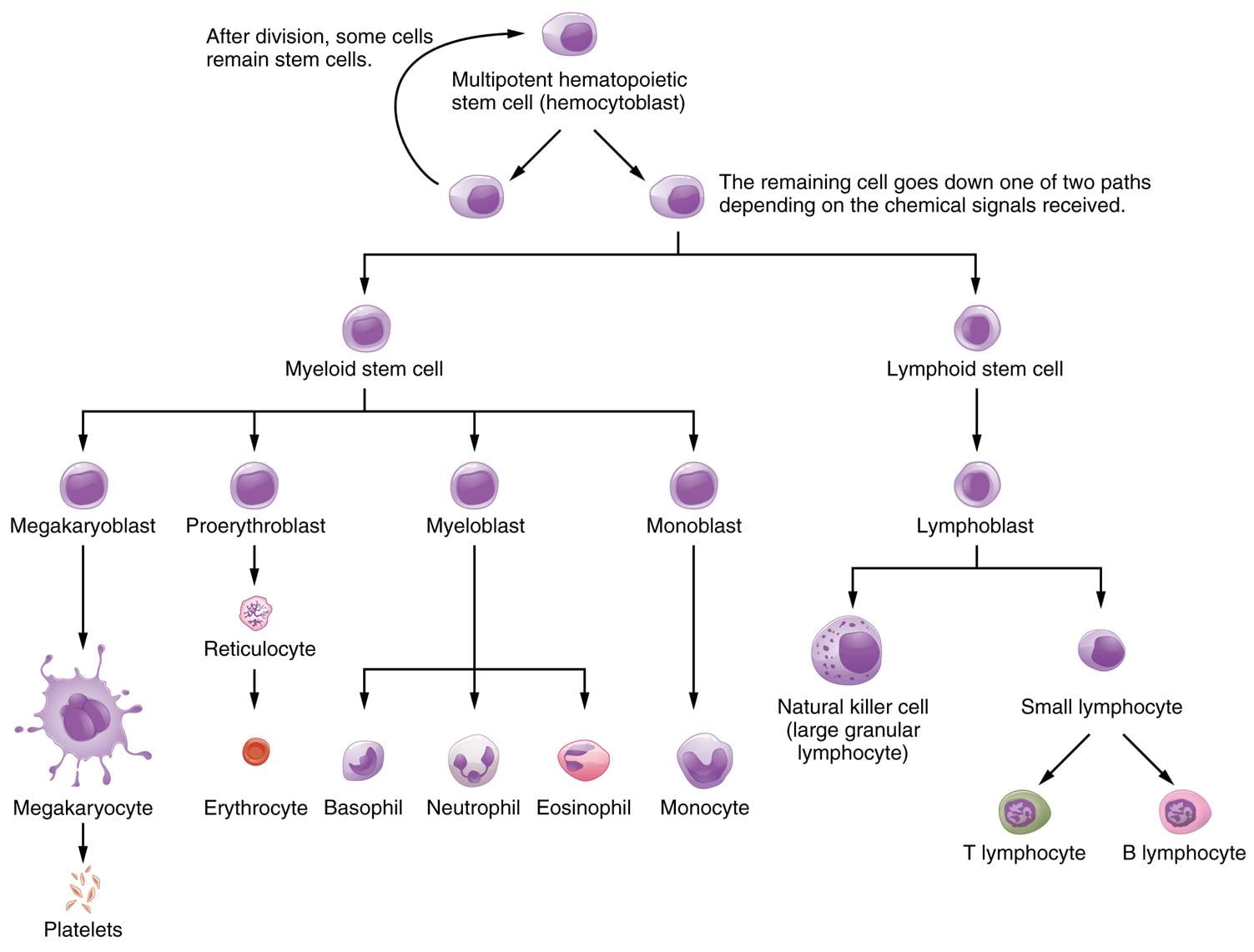
A differential WBC count can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including:
- Infection
- Inflammation
- Allergies
- Leukemia
- Lymphomas
- Immune system disorders
To perform a differential WBC count, a healthcare provider will collect a blood sample from the patient’s vein. The sample will then be stained and examined under a microscope by a trained technician. The technician will count the number of each type of WBC in the sample and report the results to the healthcare provider.
The study of blood smear for differential WBC count is a routine part of a complete blood count (CBC). A CBC is a blood test that measures the levels of different blood cells, including WBCs. The differential WBC count is a more specific test that provides more information about the types of WBCs present in the blood.
The study of blood smear for differential WBC count is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring a variety of conditions. It is a quick and painless test that can provide important insights into a person’s health.
Procedure for differential WBC count from a blood smear
The following steps involved in performing a differential WBC count from a blood smear:
- Sample Collection: A small sample of blood is drawn from a patient’s vein, typically from the arm, using a needle and syringe. This blood is then transferred onto a glass slide.
- Blood Smear Preparation: The blood on the slide is spread into a thin, even layer using a spreader slide or a technique called the “smear slide” method. This ensures that the cells are evenly distributed and not clumped together.
- Fixation: The blood smear is left to air dry, which fixes the cells onto the slide. This helps prevent distortion of cell morphology during subsequent staining.
- Staining: The dried smear is then stained using specific stains, such as the Romanowsky stains (e.g., Wright’s stain, Giemsa stain), which differentiate different cell types by color. These stains allow for better visualization of cellular structures and help distinguish different types of white blood cells based on their size, shape, and staining properties.
- Microscopic Examination: The stained slide is observed under a microscope using various magnifications. White blood cells are identified and classified based on their morphological characteristics. The different types of white blood cells include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Cell Counting: The observer systematically counts a certain number of white blood cells from different areas of the smear. This count is usually performed on a predetermined number of cells (e.g., 100 cells) to calculate the percentage of each cell type.
- Data Analysis: Once the cell counts are obtained, the percentages of different white blood cell types are calculated. These percentages provide valuable information about the patient’s immune response and overall health. Abnormalities in the distribution of white blood cells can indicate various medical conditions, such as infections, inflammation, leukemia, and more.
- Reporting: The results of the differential WBC count are typically reported as a percentage breakdown of each type of white blood cell present in the sample. This information is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a differential white blood cell count from a blood smear is a fundamental laboratory procedure that aids in diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. It provides important insights into the composition of white blood cells and helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care.