Cell Biology: Cell biology is a rapidly growing field, and new discoveries are being made all the time.
Cell biologists are working to develop new treatments for diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s disease. They are also working to develop new technologies such as artificial tissues and organs. Cell biology is a fascinating and important field of study. By understanding how cells work, we can better understand how living organisms work and how to treat diseases.
What is Cell Biology?
Cell biology, also known as cytology, is the branch of biology that examines the structure, function, and behavior of cells, the fundamental units of life. It encompasses various aspects, including cellular organization, molecular processes, cell division, and interactions between cells and their environment. Cell biology is the study of the structure, function, and behavior of cells. Cells are the basic units of life, and they make up all living organisms, from simple bacteria to complex plants and animals. Cell biology is a broad field that encompasses many different topics, including:
Cell structure: Cell biologists study the different parts of a cell and how they work together.
Cell function: Cell biologists study the different processes that occur within a cell, such as metabolism, cell division, and cell signaling.
Cell behavior: Cell biologists study how cells interact with each other and with their environment.
Structure of a Cell
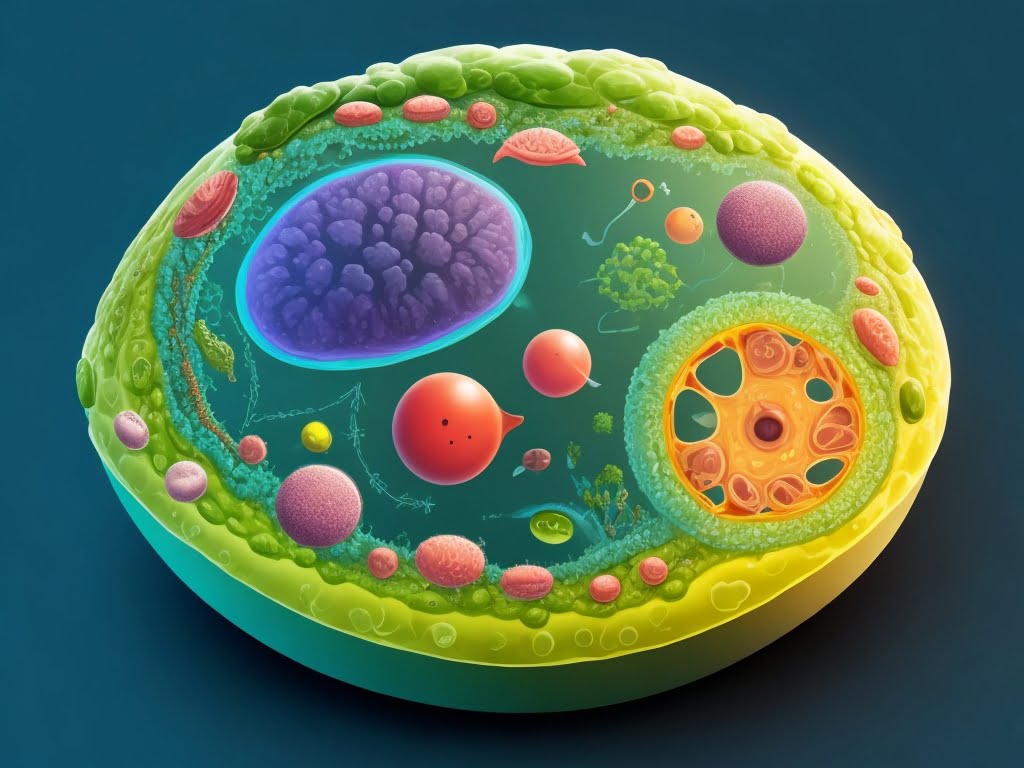
Cells exhibit a remarkable diversity in their structures, but they share some common features. Understanding the components of a cell is essential to comprehend its functions fully.
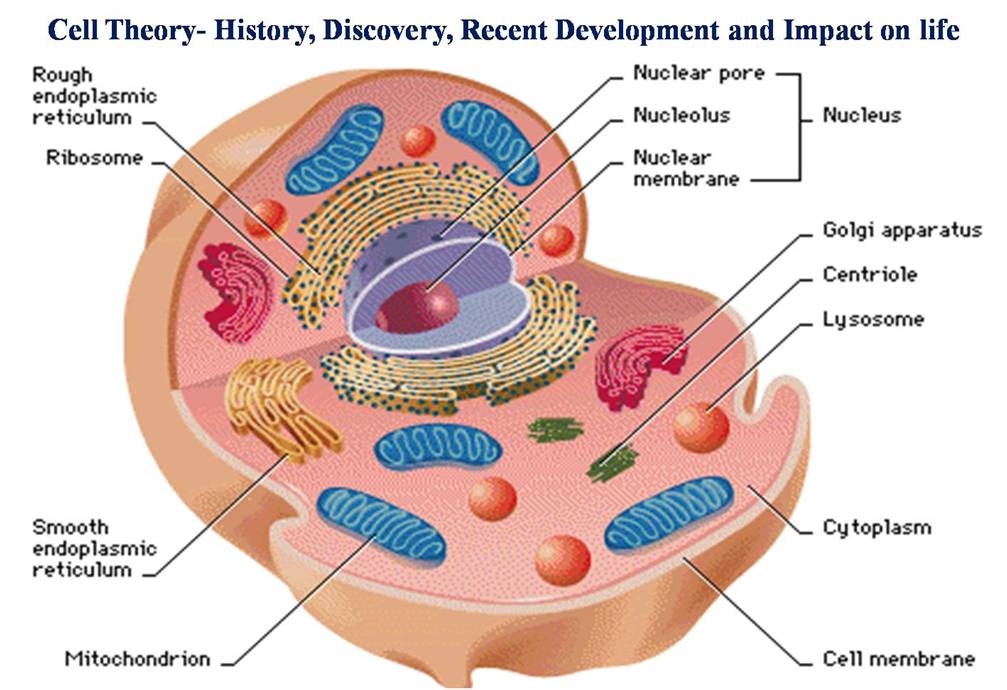
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a crucial component of all cells. It acts as a selectively permeable barrier, controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell. The membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins that facilitate various cellular processes. It also plays a vital role in cell communication and signal transduction.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell, surrounding its internal structures. It contains various organelles, dissolved nutrients, and other essential molecules necessary for cellular activities. Many metabolic reactions take place in the cytoplasm, supporting the cell’s overall functioning.
Nucleus
The nucleus is often referred to as the cell’s control center. It houses the cell’s genetic material, including DNA, which carries the instructions for cell growth, reproduction, and functioning. The nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, a double-membrane structure that regulates the flow of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Organelles
Organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions. They are like tiny organs that contribute to the overall cell physiology. Some essential organelles include:
Mitochondria: Responsible for energy production through cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: Involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport within or outside the cell.
Lysosomes: Contain enzymes for digestion and waste removal.
Chloroplasts (in plant cells): Facilitate photosynthesis by capturing light energy.
Cell Types
There are two primary types of cells based on their internal structures:
Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are simple, single-celled organisms without a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. They are typically smaller and less complex than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and archaea are examples of prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells. They possess a true nucleus, where the genetic material is enclosed within a membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain various organelles that carry out specific functions. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are examples of eukaryotic organisms.
Cell Functions and Processes
Cells are remarkable entities that perform a multitude of functions to sustain life. Here are some essential cellular processes:
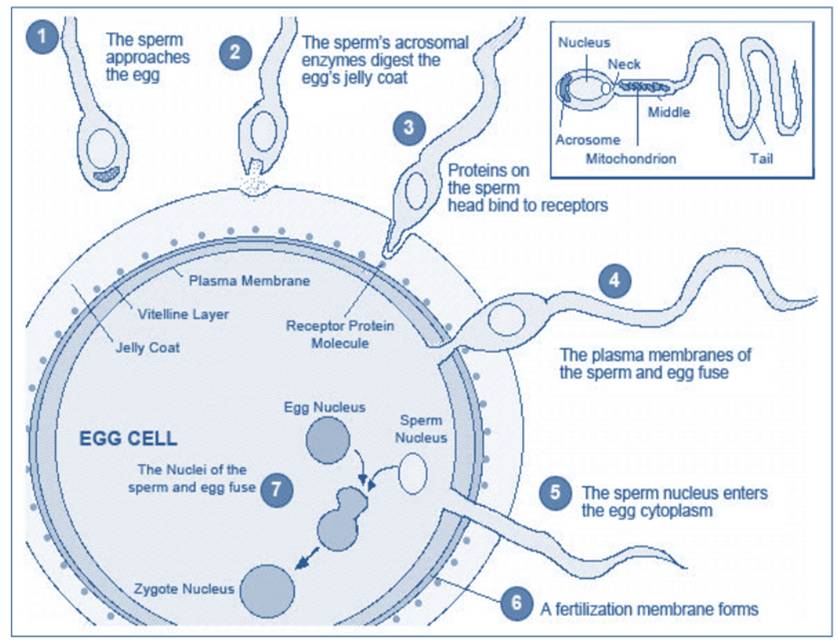
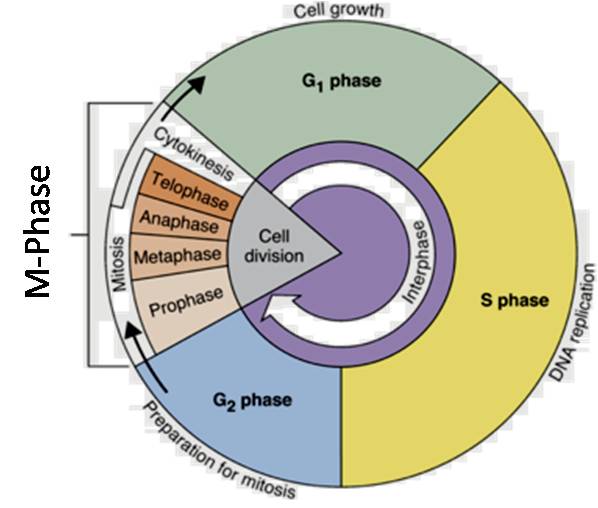
Cell Division
Cell division is a crucial process by which cells reproduce and multiply. It ensures the growth and repair of tissues and is essential for the development of multicellular organisms. The two main types of cell division are mitosis and meiosis.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert nutrients, such as glucose, into energy (ATP). It occurs in the mitochondria and is essential for the survival of cells and organisms.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process exclusive to plants and some algae, where they use sunlight to synthesize glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. It sustains the Earth’s oxygen levels and provides a source of food for many organisms.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create new proteins. It involves transcription (DNA to RNA) and translation (RNA to protein). Proteins play critical roles in the structure and function of cells.
Importance and new discovery of Cell
Cell biology forms the foundation for various scientific disciplines, including genetics, medicine, biotechnology, and ecology. Understanding cellular processes is crucial for advancing medical research, developing new therapies, and addressing health challenges. It also helps researchers comprehend diseases at the cellular level, leading to improved diagnostics and treatments. recently new discovery added in the study of cell as follows-
1. New cell types: Scientists are constantly discovering new types of cells within organisms. A recent example of this is the discovery of a new type of immune cell in the thymus, a gland located in the chest that plays a role in maturation of T cells . These new cells, called M cells, are very similar to M cells found in the gut and airways, but they have a different developmental origin. Understanding the function of these new M cells could lead to advances in immunology.
2. New cellular components: In addition to discovering new cell types, scientists are also finding new structures within cells. In January of 2023, researchers at Umeå University in Sweden discovered a new cellular component inside neurons that is important for our sense of smell. An example of this is a recent discovery of a new organelle, called a multivesicular transducosome, found in neurons. This organelle is thought to play a role in the sense of smell. This finding could help researchers understand why smell is sometimes impaired in conditions like COVID-19.
Multivesicular transducosome
Another interesting discovery came in 2018, when researchers at the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden found a new type of protein complex in human cells. This complex plays a part in cell division and how cells attach to their surroundings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cell biology is a captivating field that delves into the intricate workings of cells, the building blocks of life. By understanding cell structure, functions, and processes, we gain valuable insights into the mechanisms driving living organisms. This knowledge has far-reaching implications in various scientific domains, including medicine, genetics, and biotechnology.
FAQs on Cell Biology
What is the primary focus of cell biology?
The primary focus of cell biology is to study the structure, function, and behavior of cells, the basic units of life.
How does cell biology relate to genetics?
Cell biology and genetics are closely linked since genetics explores the inheritance and variation of traits through the study of genes, which are housed within cells.
Why is the cell membrane essential for cells?
The cell membrane is vital as it controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, ensuring cellular homeostasis and communication.
What are stem cells, and why are they significant in cell biology?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of transforming into specialized cell types. Their unique properties make them valuable in regenerative medicine and disease research.