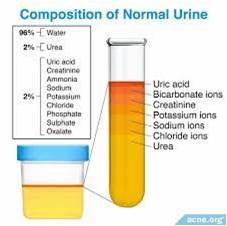
Constituents and Composition of urine: Urine is a liquid waste product excreted by the kidneys as they filter the blood. The process of removal of waste products from the body is called excretion. It is primarily composed of water, but it also contains various dissolved substances and waste products that our body needs to eliminate. It maintains the homeostasis or balance of the body against changes in the environment. Normal urine consists of water, urea, salts, and pigments. The constituents and composition of urine vary depending on a number of factors, including diet, fluid intake, medications, and underlying health conditions. Normal urine is pale yellow. Urinalysis is generally used for diagnostic procedures to detect any abnormality. However, the following are the most common constituents and composition of urine:
Physical Characteristic of Normal Urine
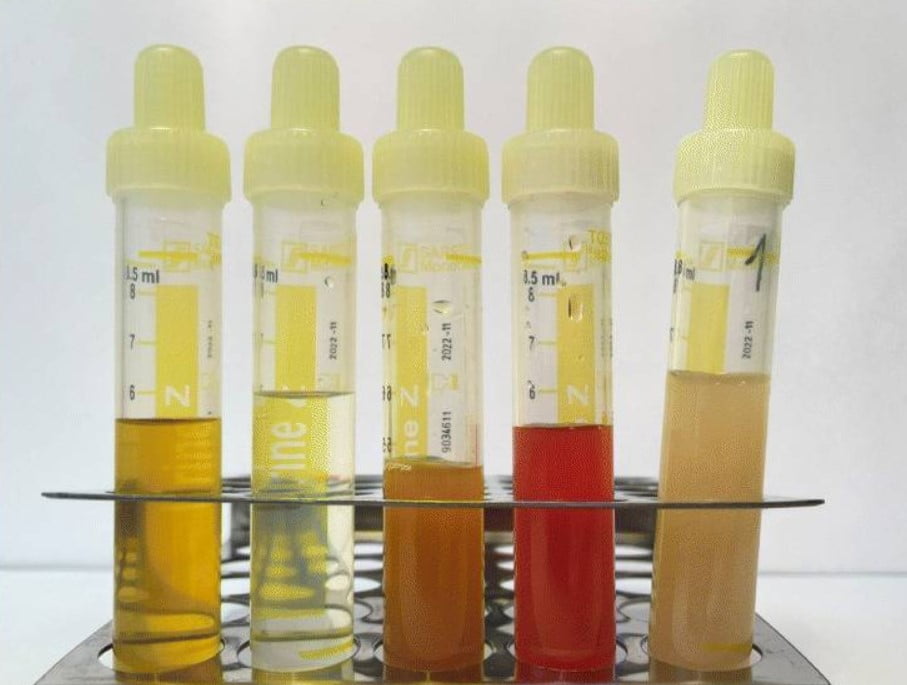
Color: The color of urine is determined by the presence of urochrome, a pigment that is produced by the breakdown of hemoglobin. The concentration of urochrome in urine is influenced by the amount of water that is present. When urine is concentrated, it is darker yellow. When urine is dilute, it is lighter yellow or clear.
Odor: The odor of urine is caused by the presence of ammonia. Ammonia is produced by the breakdown of urea. The concentration of ammonia in urine is influenced by the pH of urine. When urine is acidic, it has a stronger odor. When urine is alkaline, it has a weaker odor. ‘Constituents and Composition of urine’
Smell: Normal urine has a typical smell. The smell varies according to the food intake. The typical ammonia smell is due to the bacterial action on urea.
pH: pH level 7 is considered as neutral, whereas a pH less than 7 is acidic, and greater than seven is alkaline. Normal urine has a pH of around 6.2. However, it can range from 5.5 to 7.0. Urine is acidic if there is an uptake of a high protein-rich diet.
Volume: The normal volume of urine production is about 1-2 liters per day. However, this amount can vary depending on a number of factors, such as water intake, diet, activity level, and climate.
Constituents and Composition of urine
Water
Water makes up the majority of urine, accounting for approximately 95% of its composition. It serves as a solvent for other substances, helping transport waste out of the body.
Urea
Urea is a nitrogenous waste product resulting from the breakdown of proteins in the liver. It constitutes about 2% of urine and plays a crucial role in eliminating excess nitrogen from the body.
Creatinine
Creatinine is a waste product generated from muscle metabolism. It makes up around 2% of urine and serves as an indicator of kidney function. Elevated creatinine levels can suggest kidney problems.
Electrolytes
Urine contains various electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, and chloride. These electrolytes help regulate fluid balance and maintain the body’s electrical conductivity.
Other Substances
Other substances found in urine include uric acid, ammonia, and various metabolic byproducts. These substances can provide valuable insights into a person’s health when analyzed in a clinical setting.
- Other organic compounds: Other organic compounds found in urine include glucose, amino acids, hormones, and vitamins. These substances are present in small amounts and their levels can vary depending on a number of factors.
- Other inorganic compounds: Other inorganic compounds found in urine include pigments, salts, and gases. These substances are also present in small amounts and their levels can vary depending on a number of factors. ‘Constituents and Composition of urine’
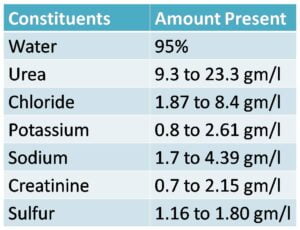
Composition of Urine:
Here are the composition of normal urine a healthy person as follows in table –
How is Urine Produced?
Urine is formed through a complex process involving the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Filtration: The kidneys filter blood, removing waste products and excess substances.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
- Concentration: Remaining waste products and excess substances are concentrated into urine.
- Storage: Urine is stored in the bladder until it is excreted.
- Excretion: Urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Factors Affecting Urine Composition
The composition of urine can vary based on several factors, including:
- Hydration: Adequate hydration dilutes urine, while dehydration leads to concentrated urine.
- Diet: What you eat can influence the presence of certain substances in urine.
- Medications: Some medications may affect urine color and composition.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Kidney and metabolic disorders can alter urine constituents.
FAQs About Urine Composition
1. Can the color of urine indicate a health problem?
A: Yes, the color of urine can provide clues about your health. Dark yellow or amber urine may indicate dehydration, while pink or red urine may signal the presence of blood, possibly due to an underlying condition.
2: What causes the ammonia-like smell in urine?
A: The ammonia-like smell in urine is often due to the breakdown of urea. However, a strong ammonia odor could be a sign of an infection or other medical issue. ‘Constituents and Composition of urine’
3: Is it normal for urine to foam?
A: A small amount of foam in urine is generally normal. However, persistent foaming could be a sign of excess protein in the urine, which may indicate kidney problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the composition of urine is essential for monitoring and maintaining your health. By recognizing the various constituents and factors affecting urine, you can gain valuable insights into your body’s functioning. Remember to stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your urine composition.