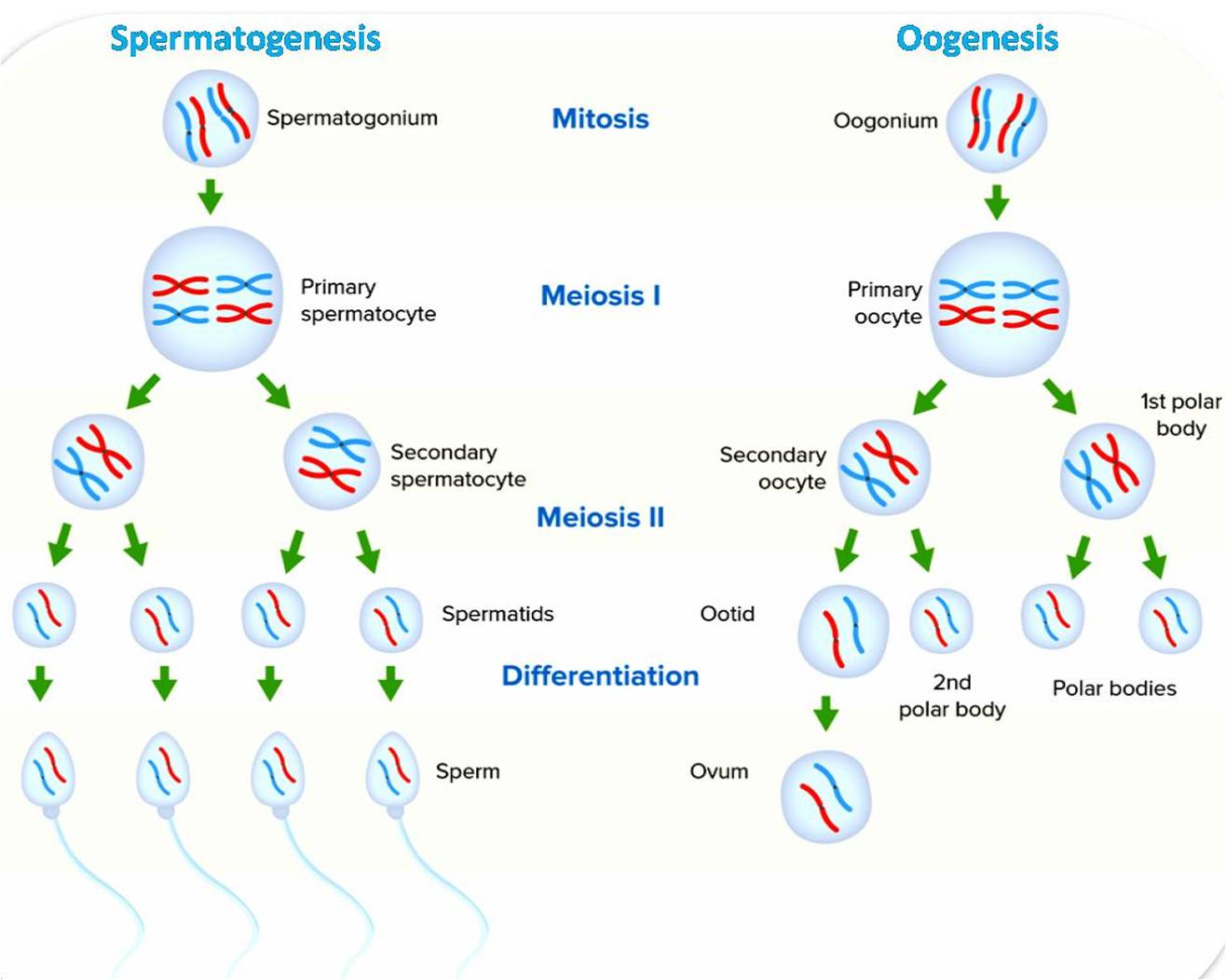
Gametogenesis: It is the process by which gametes, or sex cells, are produced. Gametes are haploid cells, meaning they contain half the number of chromosomes as a normal cell. This is necessary for sexual reproduction, as when two gametes fuse together, they form a diploid cell with the full number of chromosomes. It is a complex process that involves cell division and differentiation. In humans, gametogenesis begins at puberty and continues throughout the reproductive years. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are two types of gametogenesis. Spermatogenesis occurs in male testes and produces four functional spermatozoa from a primary spermatocyte. Oogenesis occurs in ovaries and produces a single ovum from a primary oocyte. In this article are coveres the details of gametogenesis – spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Male gametogenesis (spermatogenesis)
In males, gametogenesis begins at puberty and continues throughout the reproductive years. The testes produce sperm, which are the male gametes. Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules, which are small tubes that are located in the testes.
Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes. The process begins with a spermatogonium, which is a stem cell that gives rise to sperm. Spermatogonia undergo mitosis, a type of cell division that produces two identical cells.
Some spermatogonia differentiate into primary spermatocytes. Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis I, which reduces the number of chromosomes in half. Meiosis II follows, producing four haploid cells called spermatids.
Spermatids undergo spermiogenesis, a process of differentiation that transforms them into mature sperm cells. Sperm cells are then released from the testes in a process called ejaculation.
The process of male gametogenesis can be divided into three phases:
- Spermatogenesis: This phase begins with a spermatogonium, which is a stem cell that gives rise to sperm. Spermatogonia undergo mitosis, a type of cell division that produces two identical cells.
- Meiosis I: This phase reduces the number of chromosomes in half.
- Meiosis II: This phase produces four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original spermatogonium.
Female gametogenesis (oogenesis)
In females, gametogenesis begins at puberty and continues throughout the reproductive years. The ovaries produce eggs, which are the female gametes. Each egg is contained within a follicle, which is a sac of cells that surrounds and protects the egg.
Oogenesis occurs in the ovaries. The process begins with a primary oocyte, which is a large cell that contains all the genetic material needed to create a new individual. The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis, a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in half.
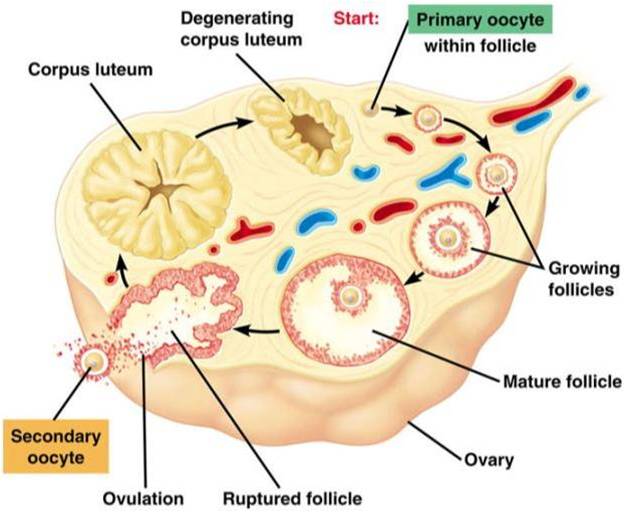
Meiosis in females begins before birth, but the process is arrested until puberty. At puberty, meiosis resumes and primary oocytes begin to mature. Each month, a few primary oocytes complete meiosis and are released from the ovaries in a process called ovulation.
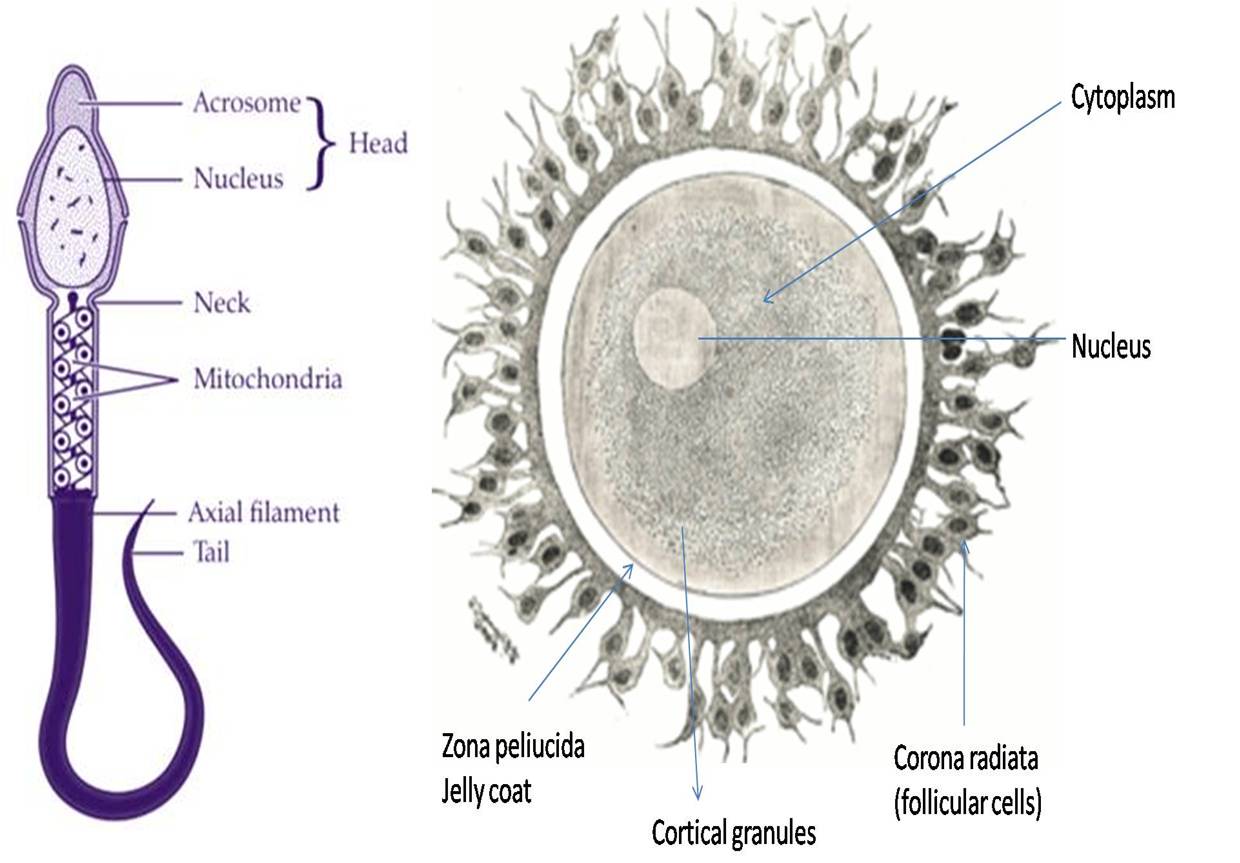
The released oocyte is now called a secondary oocyte. It is still surrounded by a layer of cells called the corona radiata. The secondary oocyte travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. If a sperm cell fertilizes the secondary oocyte, it will develop into an embryo.
The process of female gametogenesis can be divided into two phases:
- Oogenesis: This phase begins with a primary oocyte, which is a large cell that contains all the genetic material needed to create a new individual. The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis, a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in half.
- Ovulation: This phase occurs when the secondary oocyte, which is the product of meiosis, is released from the ovary. The secondary oocyte then travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it may be fertilized by a sperm cell.
The importance of gametogenesis
It is essential for reproduction. Without gametes, fertilization would not be possible and new individuals could not be created. It is also important for sexual reproduction. The genetic information from the male and female gametes is combined during fertilization to create a new individual with a unique combination of genes.
Disorders of gametogenesis
Disorders of gametogenesis can lead to infertility. Some common disorders includes:
- Ovarian failure: This is a condition in which the ovaries stop producing eggs.
- Testicular failure: This is a condition in which the testes stop producing sperm.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: These can occur during meiosis and can lead to infertility or other health problems.
Conclusion
Gametogenesis is a complex process that is essential for reproduction. In humans, gametogenesis occurs in the ovaries in females and the testes in males.