Sport fisheries: It also known as recreational or angling fisheries, refer to fishing activities undertaken primarily for pleasure, recreation, or tourism rather than for commercial gain. In India, sport fishing is a rapidly growing segment within the tourism industry, attracting both domestic and international anglers due to the country’s diverse aquatic habitats and rich fish biodiversity124.
Major Sport Fishing Regions and Sites
India’s vast network of rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and coastal waters offers year-round opportunities for sport fishing, with the best seasons varying by region:
- Himalayan Rivers: October–November and April–June are ideal for sport fishing in the Himalayan region. Notable rivers include the Beas, Ganges, Yamuna, Sutlej, and their tributaries. The Kullu-Manali region and the streams feeding the Beas River are renowned for trout angling14.
- South India: The prime season extends from April to September, with the Cauvery River being a prominent site for Mahseer fishing1.
- Kashmir: The Indus and Lidder Rivers, along with high-altitude lakes, make Kashmir an “angler’s paradise,” especially for trout fishing14.
- North-East India: Rivers and streams in this region are famous for Mahseer angling, particularly in the Ramganga and Sharda rivers near Jim Corbett National Park1.
- Marine Waters: The Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands are popular for marine sport fishing, targeting species like barramundi, tuna, and groupers4.
Sport Fisheries : Fish Species
Sport fisheries in India targets a variety of species, both indigenous and exotic:
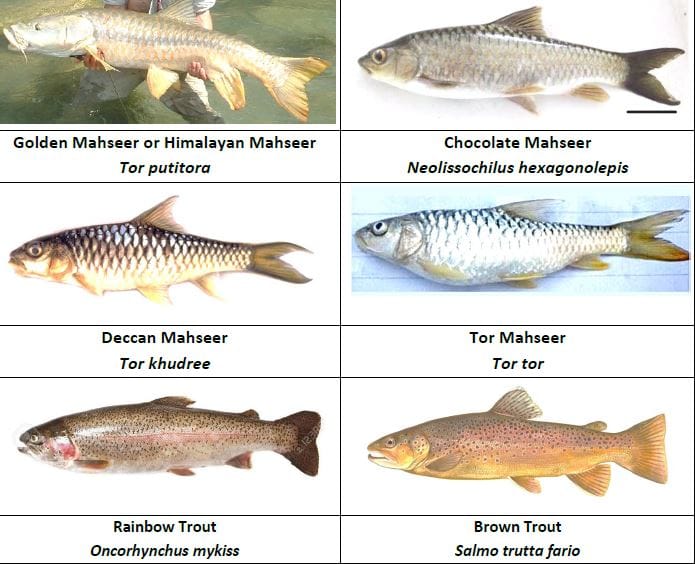
- Mahseer (Tor spp.): Known as the “King of Indian Sportfish” or “Tiger in Water,” the Golden Mahseer (Tor putitora) is highly prized for its size, strength, and fighting ability—sometimes exceeding 2.7 meters in length and 50 kg in weight146.
- Trout (Brown and Rainbow Trout): Introduced in the early 20th century, trout thrive in the cold streams of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Kashmir, attracting anglers from around the world146.
- Carps: Both indigenous and exotic carps are targeted, especially in reservoirs and lakes46.
- Large Catfishes (e.g., Bagarius bagarius or goonch): These are also sought after for their size and challenge46.
- Marine Species: Caranx ignobilis (giant trevally), Lates calcarifer (barramundi), Sphyraena spp. (barracuda), and various tunas are popular among marine anglers4.
Organizations and Regulation
Several organizations and government bodies manage and promote sport fisheries in India:
- All India Game Fishing Association: Plays a pivotal role in promoting angling and conservation efforts, with regional affiliates across the country4.
- State Fisheries Departments: Issue permits, manage hatcheries (e.g., Golden Mahseer hatchery in Himachal Pradesh), and enforce regulations14.
- Local Angling Associations: Such as the Maharashtra State Angling Association (MSAA), help regulate angling activities and promote sustainable practices4.
Regulatory frameworks are based on the Indian Fisheries Act, 1897, and local rules. There are also seasonal bans (e.g., 61-day monsoon ban in Western maritime states) to protect fish during breeding periods4.
Conservation and Challenges
Sport fisheries in India face several challenges:
- Threats: Overfishing, poaching, habitat degradation, river basin projects, and pollution threaten sport fish populations and their habitats4.
- Conservation Efforts: Hatchery programs, stocking, and ranching initiatives (notably for Mahseer and trout) aim to replenish stocks and support sustainable angling14.
- Awareness and Research: There is a need for greater awareness, scientific research, and region-specific management to conserve threatened and endangered sport fish species4.
Economic and Social Importance
- Tourism and Recreation: Sport fishing is a significant draw for eco-tourism, supporting local economies and promoting conservation awareness124.
- Community Engagement: Angling associations and local communities benefit from regulated sport fisheries through permit fees, tourism services, and conservation incentives4.
Summary Table: Key Aspects of Sport Fisheries in India
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Main Regions | Himalayas, South India, Kashmir, North-East, Andaman & Nicobar Islands |
| Major Species | Mahseer, Trout, Carps, Catfishes, Marine game fish |
| Best Seasons | Himalayas: Oct-Nov, Apr-Jun; South India: Apr-Sep; Marine: Oct-Apr |
| Key Organizations | All India Game Fishing Association, State Fisheries Departments, local angling clubs |
| Conservation Efforts | Hatcheries, stocking/ranching, seasonal bans, awareness campaigns |
| Challenges | Overfishing, habitat loss, pollution, lack of regulation/enforcement |
Sport fisheries in India offer unique recreational opportunities, support biodiversity conservation, and contribute to rural and eco-tourism, but require continued management and awareness to ensure their sustainability147.
Read more: Fish Seed Collection