Sanitation and HACCP: Sanitation and HACCP share the same goal of producing safe food products, the focus of sanitation is on the environment surrounding the food to prevent contamination, whereas the focus of HACCP is on controlling hazards intrinsic to food materials. Together they provide the organizational base for applying the correct methods and procedures to ensure and verify that food served is safe for foodservice clients.
Sanitation and HACCP in Fish and Fishery Products
Ensuring the safety of fish and fishery products throughout the entire supply chain, from catching or harvesting to reaching consumers, is crucial. Two important measures that work hand-in-hand to achieve this goal are sanitation and HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point).
Sanitation
It refers to the practices and procedures implemented to maintain a clean and hygienic environment throughout the fish processing chain. This includes:
- Proper cleaning and disinfection of equipment and surfaces that come into contact with fish, to prevent contamination with harmful microorganisms.
- Maintaining proper hygiene practices for personnel involved in handling fish, such as wearing appropriate clothing, washing hands regularly, and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Implementing effective pest control measures to prevent contamination by insects, rodents, and other pests. ‘Sanitation and HACCP’
- Ensuring proper storage conditions for fish, including maintaining appropriate temperatures and preventing cross-contamination with other products.
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)
It is a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards that are reasonably likely to occur in food production and that could affect food safety. In the context of fish and fishery products, HACCP plans typically address hazards such as:
- Microbial hazards: These include bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause foodborne illness.
- Chemical hazards: These include toxins that can occur naturally in some fish species, as well as environmental contaminants.
- Physical hazards: These include foreign objects, such as bones, scales, or metal fragments, that could be present in the final product.
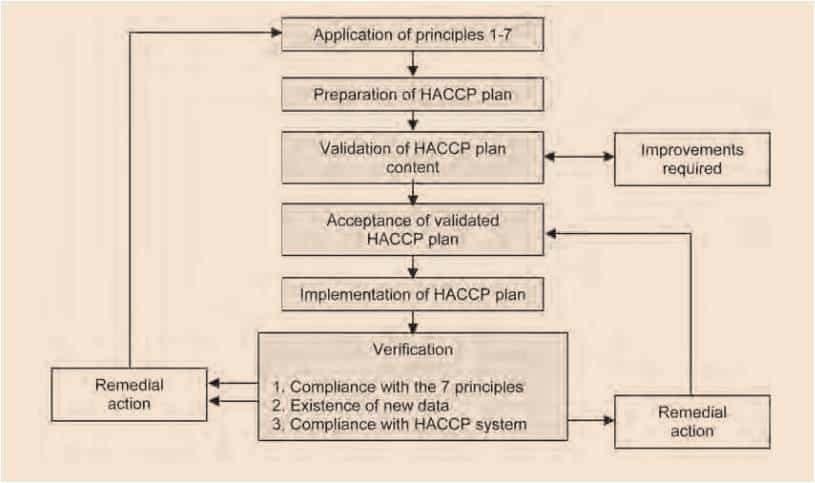
implementation of HACCP in Fish and Fishery Products
Several stages are involved in implementation of HACCP in any food, including fish and
fishery products. These are pre-requisite programme, HACCP plans, preliminary steps and
the seven principles.
Pre-requisite programmes
PRP such as SOP, SSOP, GMP, etc. are implemented prior to HACCP plans. PRP focus on
employees, facilities and equipment and deals with illness policy, cleaning and sanitizing
procedures, garbage removal, pest control, equipment selection, employee hygiene. It also
deals with control of harvest operation and the overall plant environment which are not directly related to food (e.g. water quality, transportation and storage, plant sanitation,
employee training, etc.). ‘Sanitation and HACCP’
HACCP plans
It is a document prepared in accordance with the principles of HACCP to ensure control of
hazards that are significant for food safety in the segment of the food chain under
consideration. It is implemented following pre-requisite programmes. Prior to the application of HACCP to a fish or seafood establishment, that establishment should be operating proper prerequisite programmes according to the Recommended International Code of Practice –General Principles of Food Hygiene (CAC/RCP1-1969, Revision 2008/2020).
Preliminary Steps for the introduction of a HACCP System
Gathering the resources and information needed. The application of HACCP principles
consists of the following tasks as identified in the logic sequence for the application of
HACCP (CAC, 2003/2008). ‘Sanitation and HACCP’
- Assemble the HACCP team.
- Describe product.
- Identify intended use.
- Construct flow diagram.
- Confirm flow diagram.
- Conduct hazard analysis.
- Determine CCPs (decision tree).
- Establish critical limits for each CCP.
- Establish a monitoring system for each CCP.
- Establish corrective action.
- Establish verification procedures.
- Establish documentation and record-keeping.
Seven Principles for Implementation of HACCP
- Conduct a hazard analysis: Identify all potential hazards associated with the fish and fishery product.
- Identify critical control points (CCPs): These are the points in the process where control measures can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to an acceptable level.
- Establish critical limits for each CCP: These are the specific parameters (e.g., temperature, time) that must be met to ensure the control of the hazard at the CCP.
- Monitor CCPs: Continuously monitor CCPs to ensure that critical limits are being met. ‘Sanitation and HACCP’
- Take corrective action: If a deviation from a critical limit occurs, take corrective action to bring the process back under control.
- Verify the HACCP system: Regularly verify that the HACCP system is working effectively.
- Maintain records: Maintain documentation of all HACCP records, including monitoring data, corrective actions taken, and verifications performed.
Conclusion:
By implementing effective sanitation practices and a comprehensive HACCP plan, fish processors can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illness and ensure the safety of their products for consumers.