Protozoa: Protozoans are single-celled eukaryotic organisms that are found in a variety of habitats, including water, soil, and the bodies of animals. They can be classified into four main groups based on their locomotion: flagellates, ciliates, amoebae, and sporozoans.
The slides are used to study the morphology of protozoans under a microscope. The slides are usually prepared by staining the protozoans with a dye, such as methylene blue or carmine. This makes the single cell animal more visible under the microscope and allows you to see their different structures.
There are many different types of protozoans, and they can be found in a variety of habitats, including water, soil, and the bodies of animals. Some protozoans are harmless to humans, while others can cause diseases. Protozoan slides can be used to identify different types of protozoans, to study their morphology, and to investigate their behavior. They can also be used to diagnose diseases caused by protozoans.
Protozoa: Slides from Ciliates, Opalinates, and Flagellates
Some common types of protozoan, slides include:
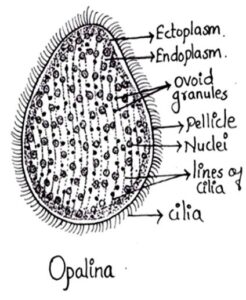
1. Opalina Purkinye & Valentin, 1835
Classification
- Kingdom: Chromista
- Subkingdom: Protista
- Phylum: Sarcomastigophora
- Subphylum: Sarcodina
- Class: Opalinea
- Order: Opalinida
- Family: Opalinidae
- Genus: Opalina
Comments:
- Commonly referred as rectal ciliate
- Body is simple oval and flattened
- Measures upto 400-500µ in diameter
- Whole body is covered with cilia
- Opalina is multinucleated.
- Found in rectum of Amphibians
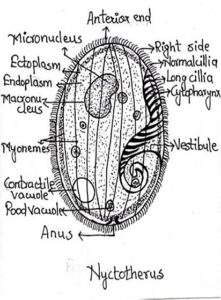
2. Nyctotherus
- Kingdom: Protista
- Subikingdom: Baciliata
- Phylum: Ciliophora
- Subphylum: Intramacronucleata
- Class: Spirotrichea
- Order: Clevelandellida
- Family: Nyctotheridae
- Genus: Nyctotherus
Comments:
- Found in alimentary canal of cockroaches, fishes, amphibians and mammals
- Body bean shaped and dorsoventrally flattened
- Measures upto 60-120 µ in diameter
- Clear distinction between ectoplasm and endoplasm
- Two nuclei are present, micro and macronucleus
- Body covered with cilia.
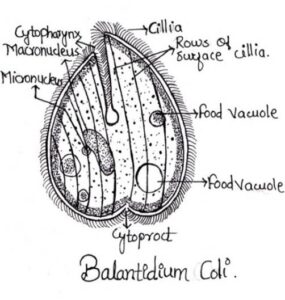
3. Balantidium coli
Classification
- Kingdom: Protista

- Phylum: Ciliophora
- Class: Litostomatea
- Order: Vestibuliferida
- Family: Balantidiidae
- Genus: Balantidium
- Species: coli
Comments:
- Commonly found in the intestine of pigs, sheep, camels, ostrich, cockroaches and man
- Spherical in shape and motile
- Measures 60-70 µ in diameter
- Body covered with spiral rows of cilia
- Endoplasm contains micronucleus and sausage shaped macronucleus.
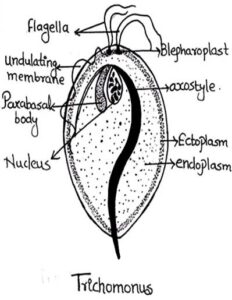
4. Trichomonas
Classification
- Kingdom: Protista
- Phylum: Metamonada
- Class: Parabasillia
- Order: Trichomonadida
- Family: Trichomonadidae
- Genus: Trichomonas
- Species: vaginalis
Comments:
- Found in intestine of vertebrates, leeches and termites and in man it is found in vagina, colon and buccal cavity
- Body oval, egg shaped slightly tapering posteriorly
- 5-20 µ in length
- 3-5 flagella are present
- Flagellum arising from the left blepharoplast forms the undulating membrane.
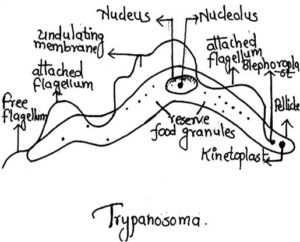
5. Trypanosoma
Classification
 Kingdom: Protista
Kingdom: Protista- Phylum: Sarcomastigophora
- Class: Zoomastigophorea
- Order: Trypanosomatida
- Family: Trypanosomatidae
- Genus: Trypanosoma
Comments:
- It is the blood parasite of man
- Body elongated, leaf like, flattened and tapering at both the ends
- Measures 10-40 µ in length and 2-10 µ in breadth
- Single flagellum running along the edge of undulating membrane
- Large central nucleus with nucleolus is present.